Java安全-代码审计
前言
java学完忘完了,从头捡起来…顺便记录一下
仅记录自己学习中觉得值得记录的地方,并不完全,也不适合所有人
环境
java:jdk17lts
编辑器:idea
基础语法
变量

1 | package com.chenci.hello; |

1 | package com.chenci.variable; |
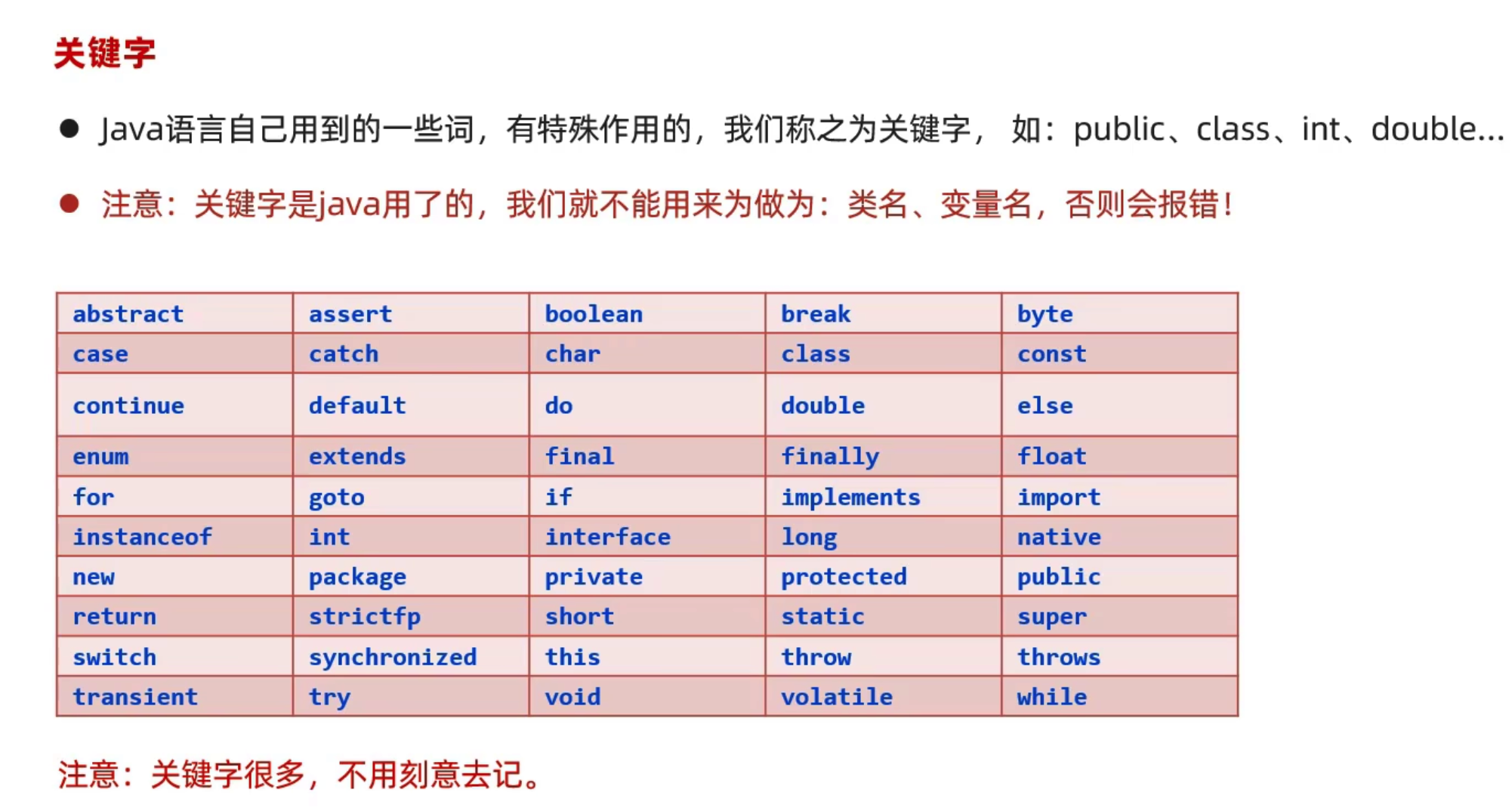
关键字
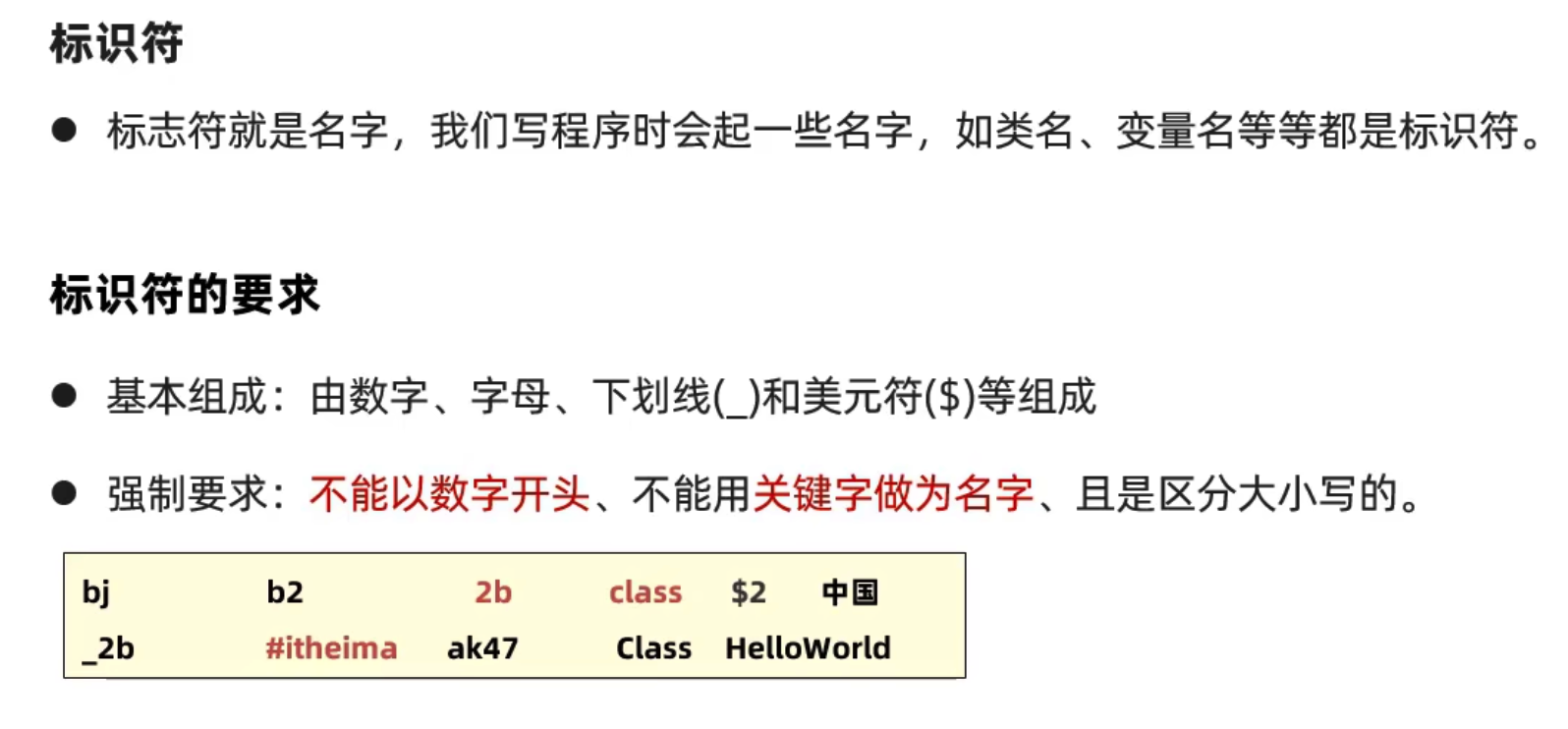
标识符
八/十六进制

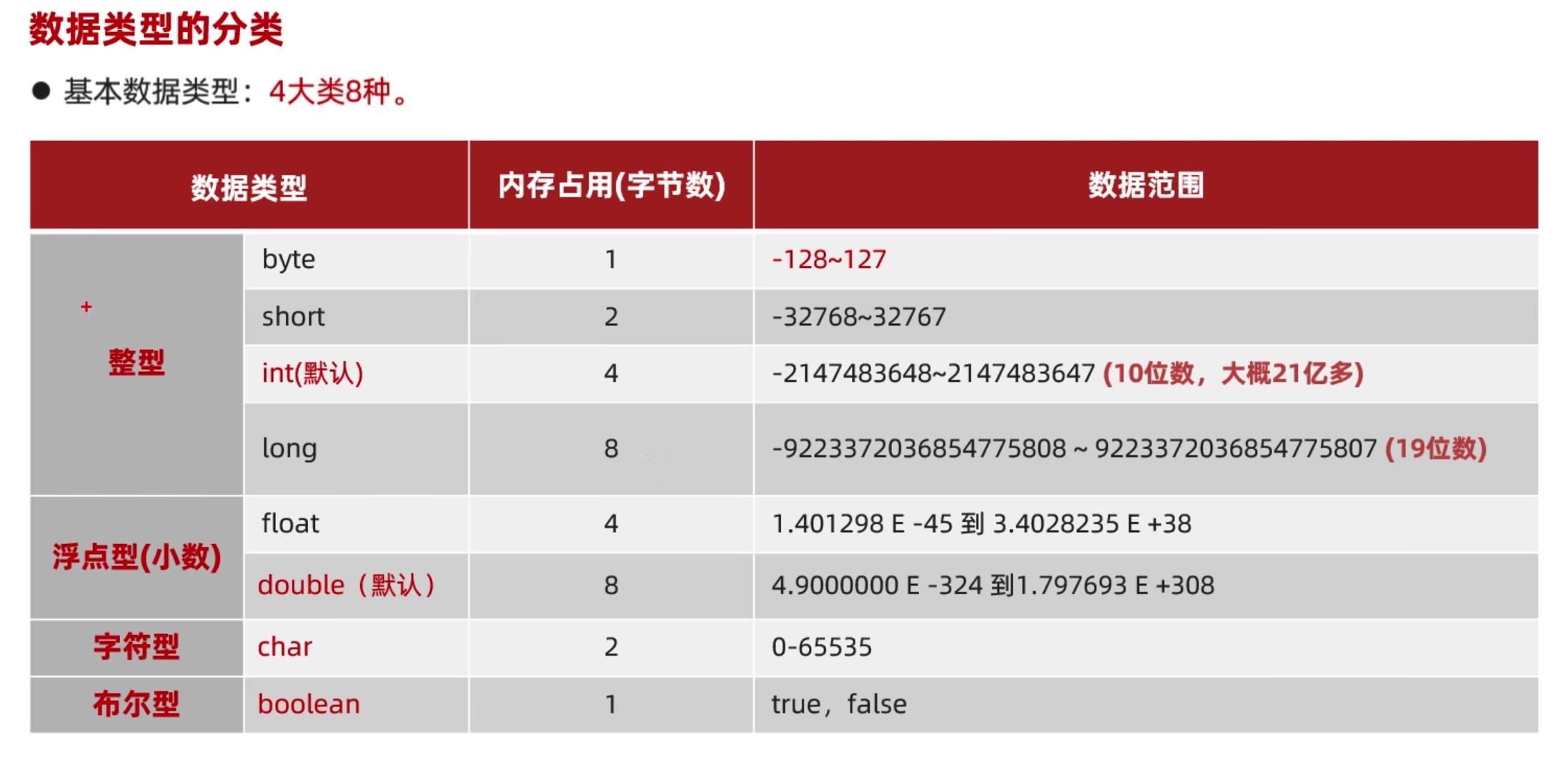
基本数据类型
1 | package com.chenci.variable; |
自动类型转换

1 | package com.chenci.variable; |
表达式自动类型转换

1 | package com.chenci.variable; |
强制类型转换

1 | package com.chenci.variable; |

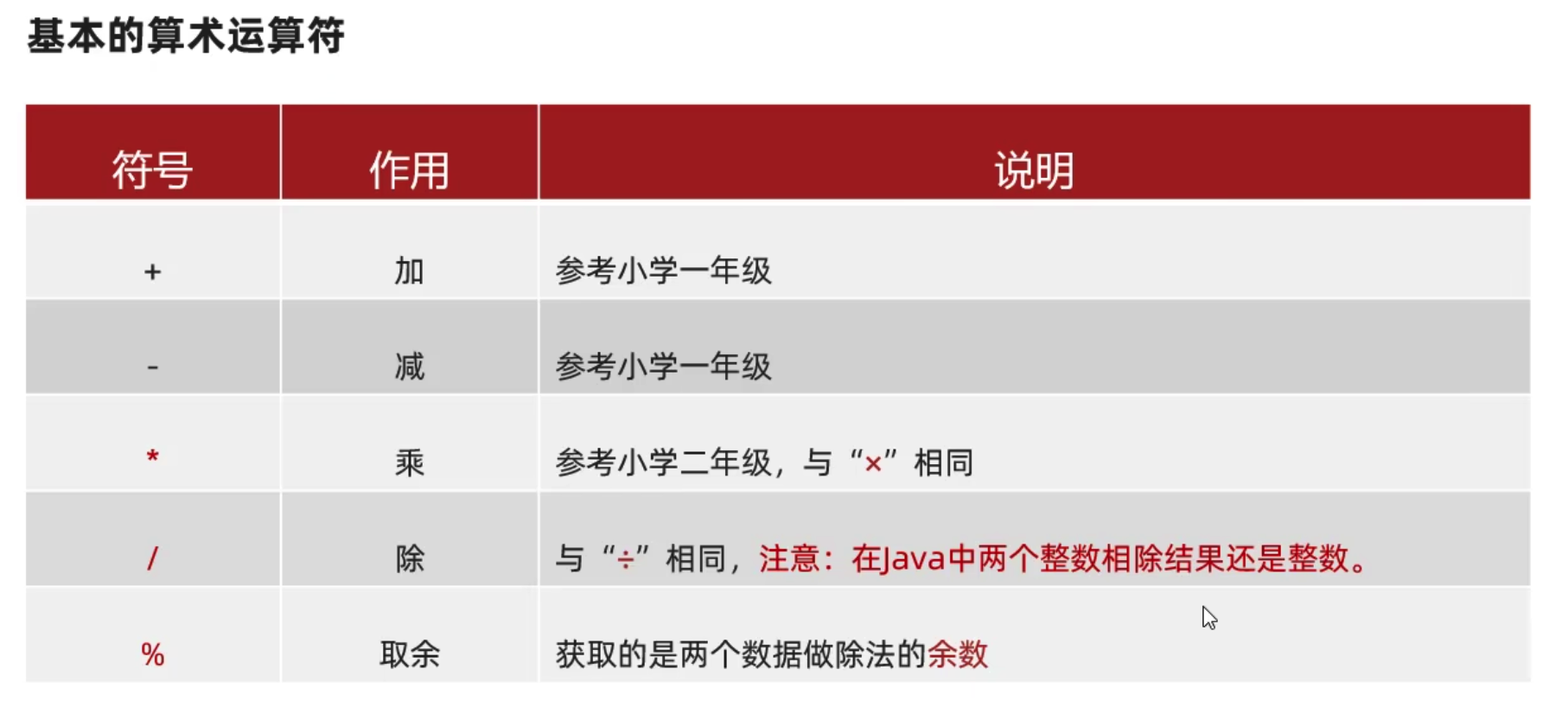
算术运算符
1 | package com.chenci.variable; |
自增自减运算符

1 | package com.chenci.variable; |
赋值运算符
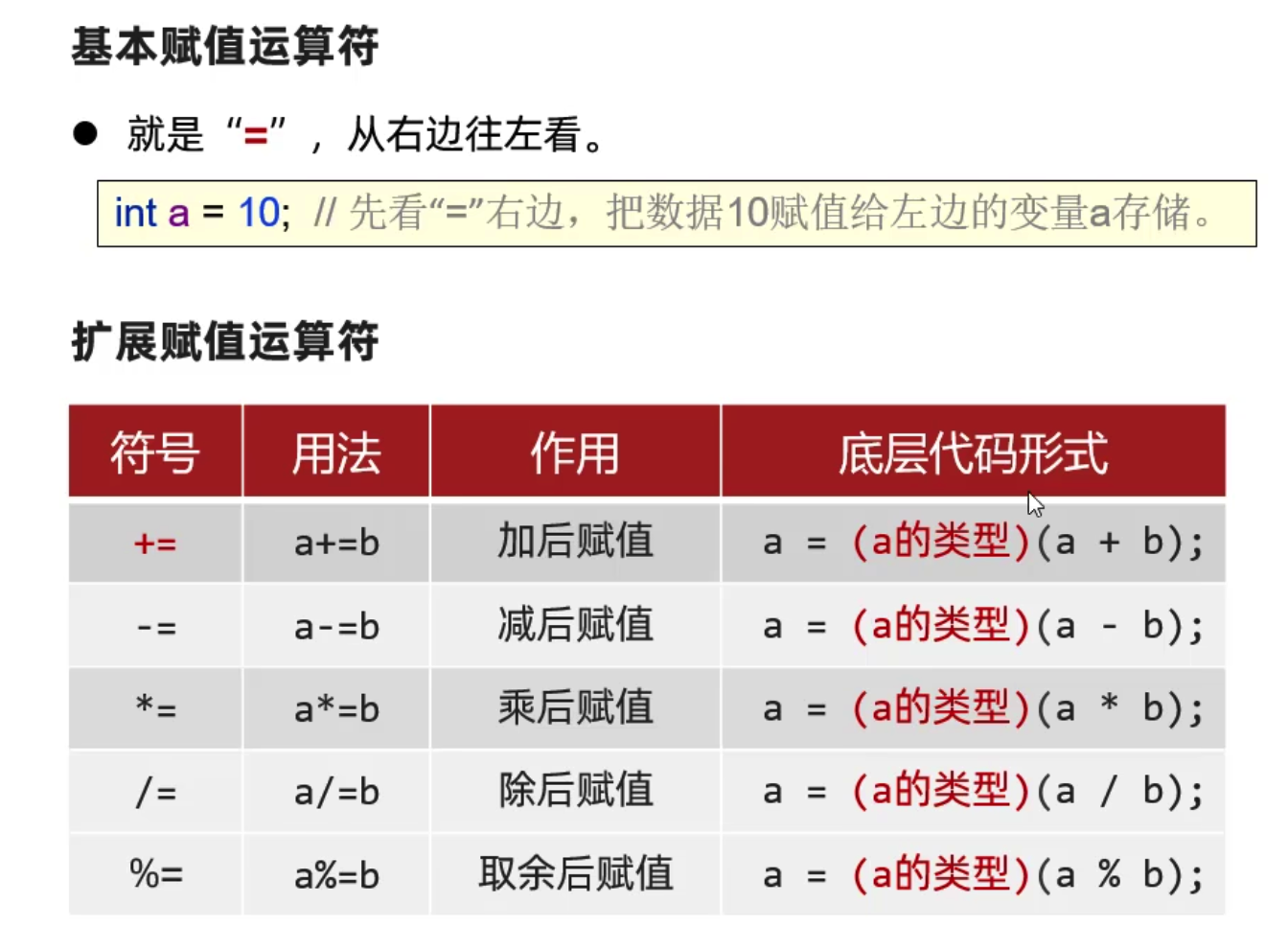
1 | package com.chenci.variable; |
1 | package com.chenci.variable; |
关系运算符
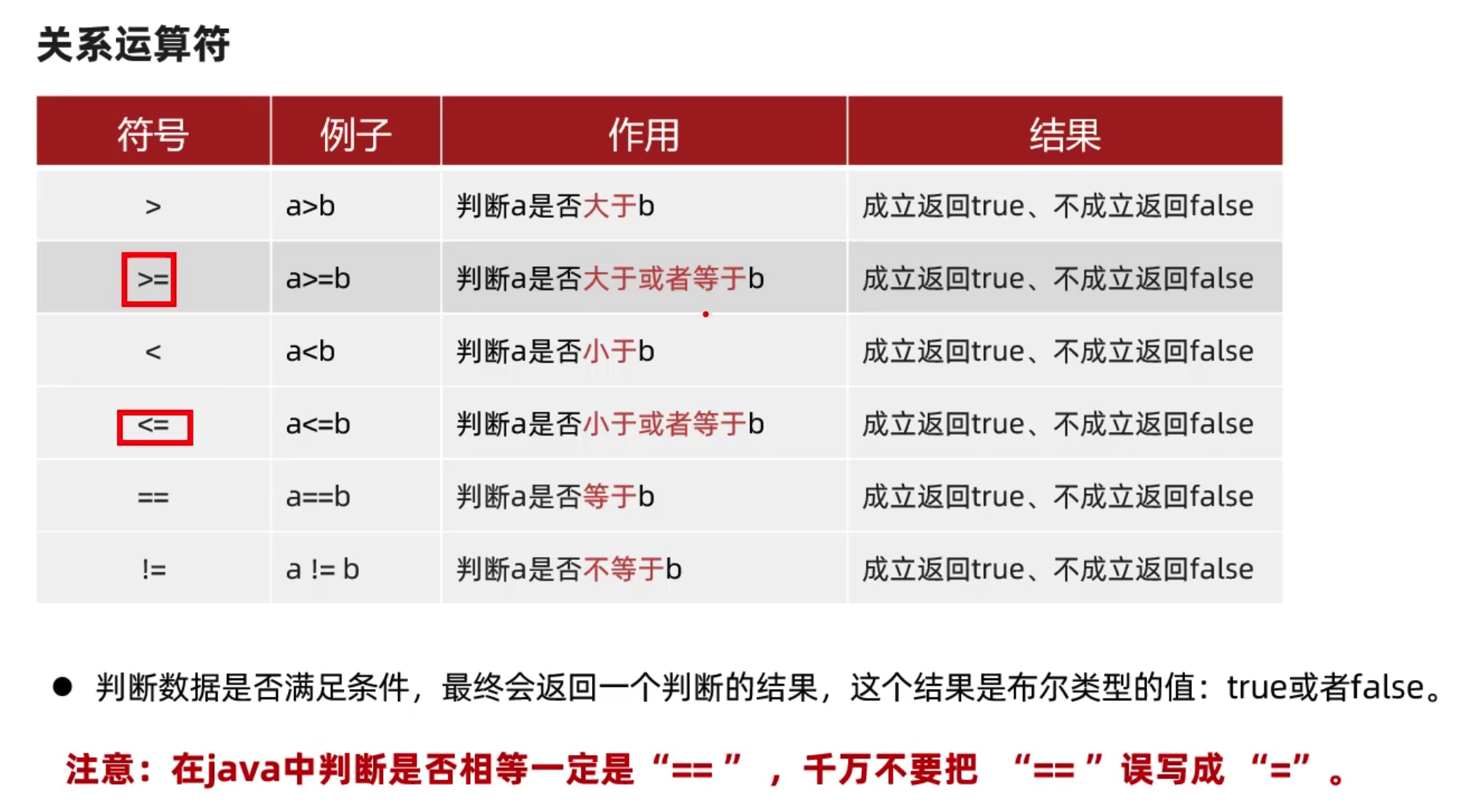
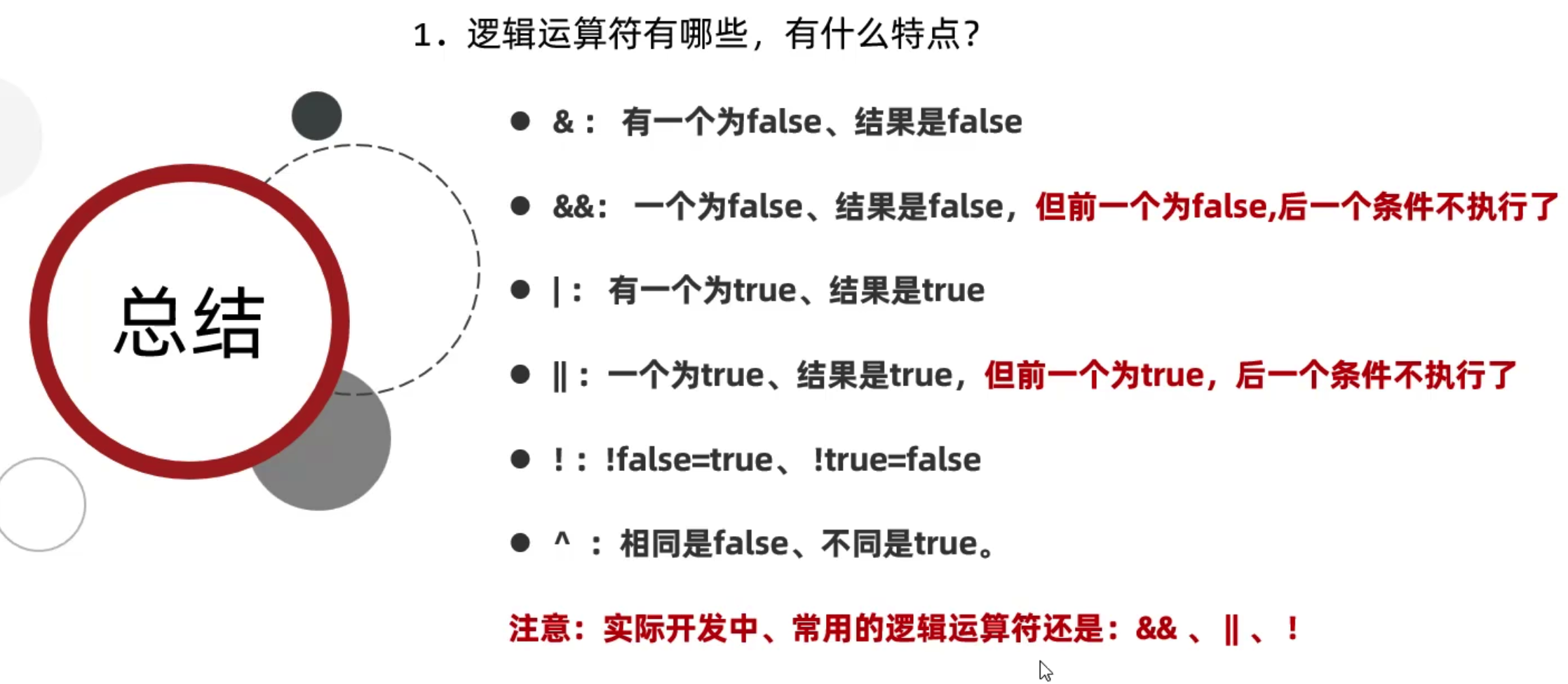
逻辑运算符
1 | package com.chenci.variable; |
三元运算符
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
运算符优先级

键盘输入
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
分支结构
if结构
1 | public class IfDemo1 { |
else if结构
1 | public class IfDemo1 { |
switch
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
或者
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |

for循环
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
while循环
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
do while循环
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |


跳转关键字

随机数
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
猜数字
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
数组
静态数组定义和访问
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
简写
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |

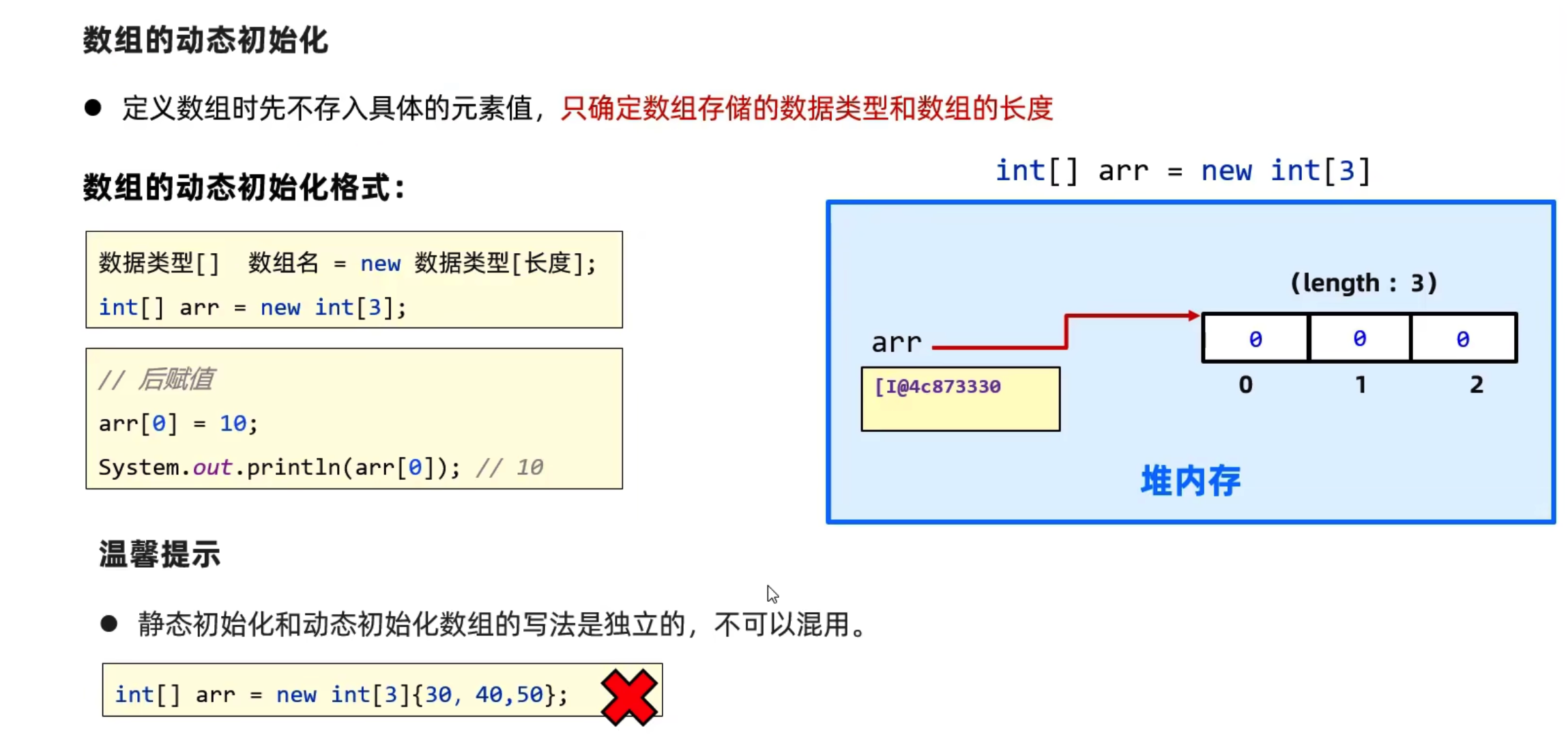
动态数组
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
数组最大值
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
数组反转
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
数组随机
1 | public class ArrayRand { |
方法
自定义方法

1 | public class Demo1 { |

求和自定义方法
1 | public class Demo2 { |
参数传递机制
基本类型参数传递
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |

引用类型参数传递
1 | public class Demo3 { |

判断两个数组是否相等
1 | public class Demo4 { |
方法重载

1 | public class Demo5 { |
案列
买飞机票

1 | public class fly { |
验证码

1 | public class code { |
打分

1 | public class dafen { |
copy数组

1 | public class copyArray { |
抢红包
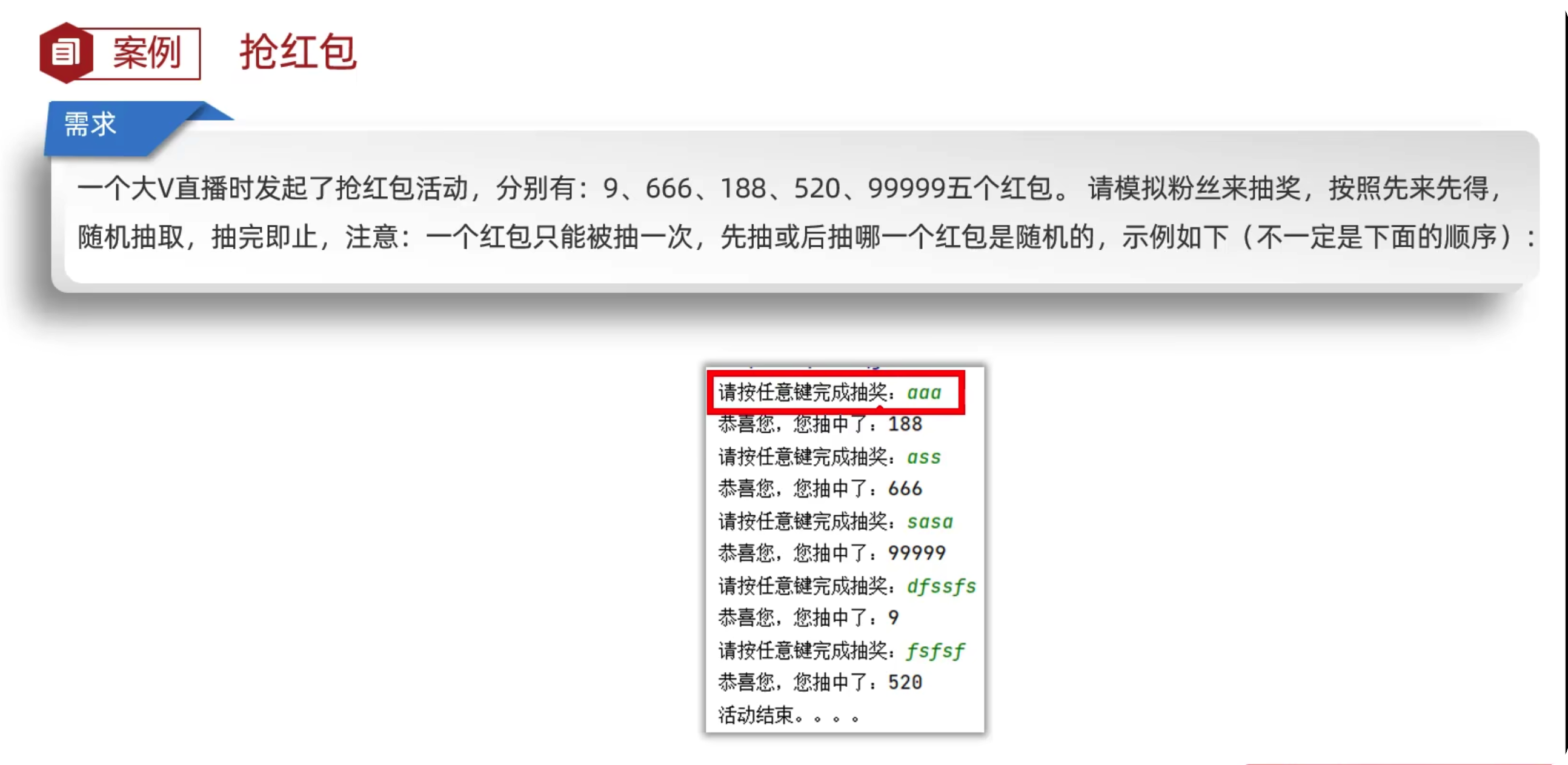
1 | public class redbao { |
素数

1 | public class sushu { |
99乘法表
1 | public static void main(String[] args) { |
面向对象

1 | public class Student { |
1 | public class test1 { |

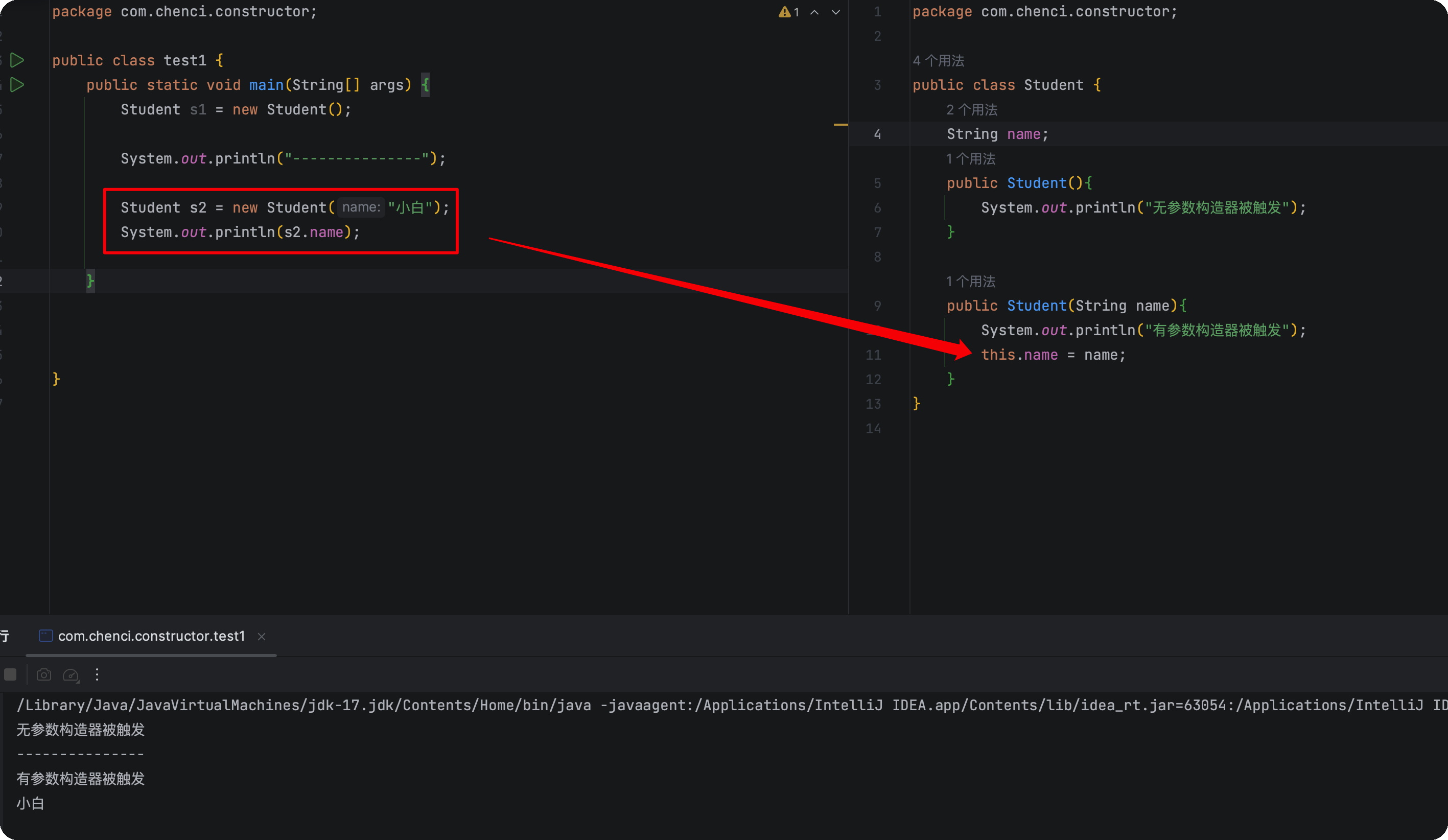
this关键字

1 | public class Student { |
1 | public class Test { |

this访问当前对象的成员变量
1 | Student s3 = new Student(); |
1 | public void printPass(double score){ |
构造器

1.构造器要和类名相同
2.构造器无返回值
1 | public class test1 { |
1 | public class Student { |
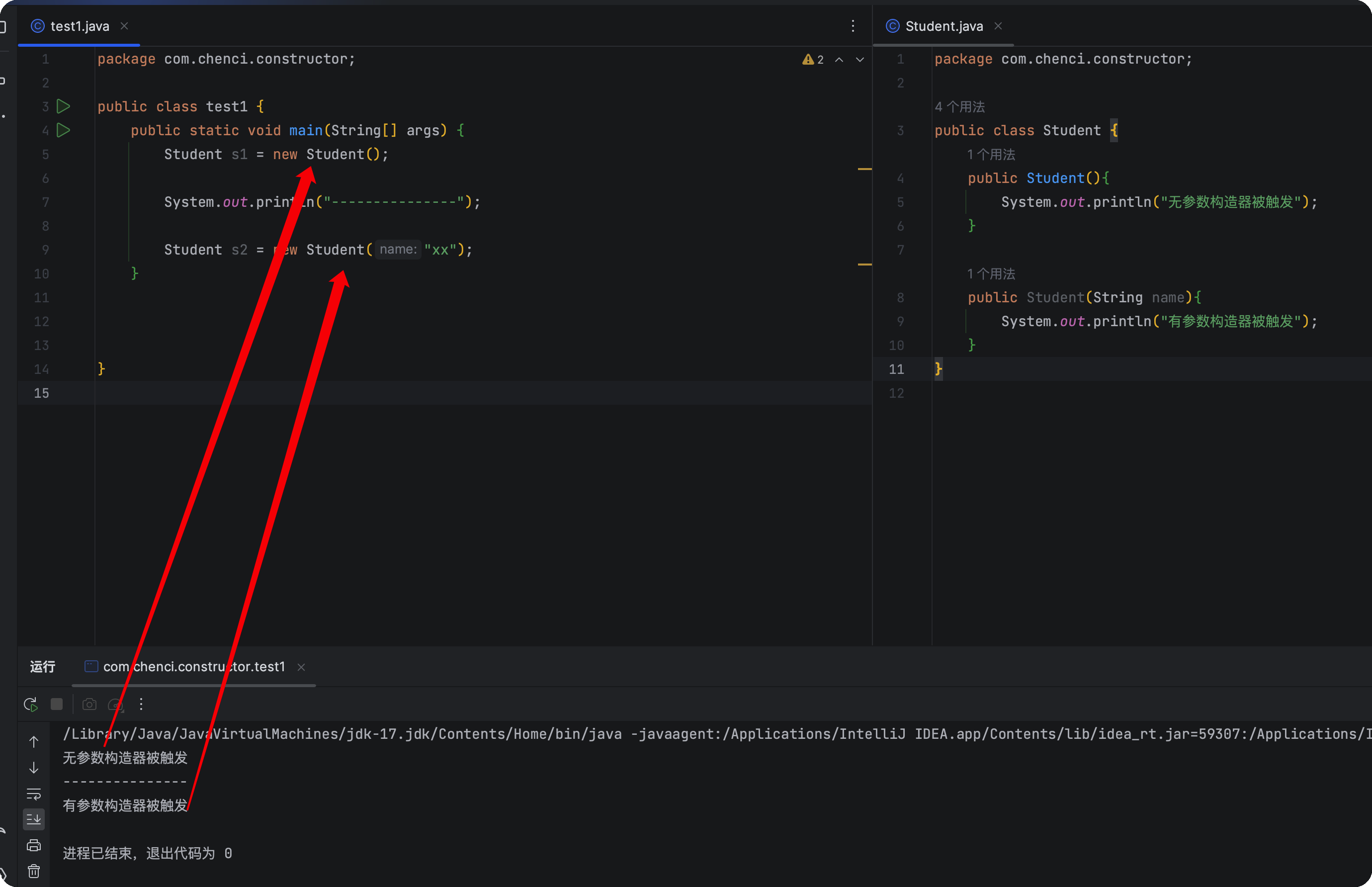
使用实例
封装
私有成员变量
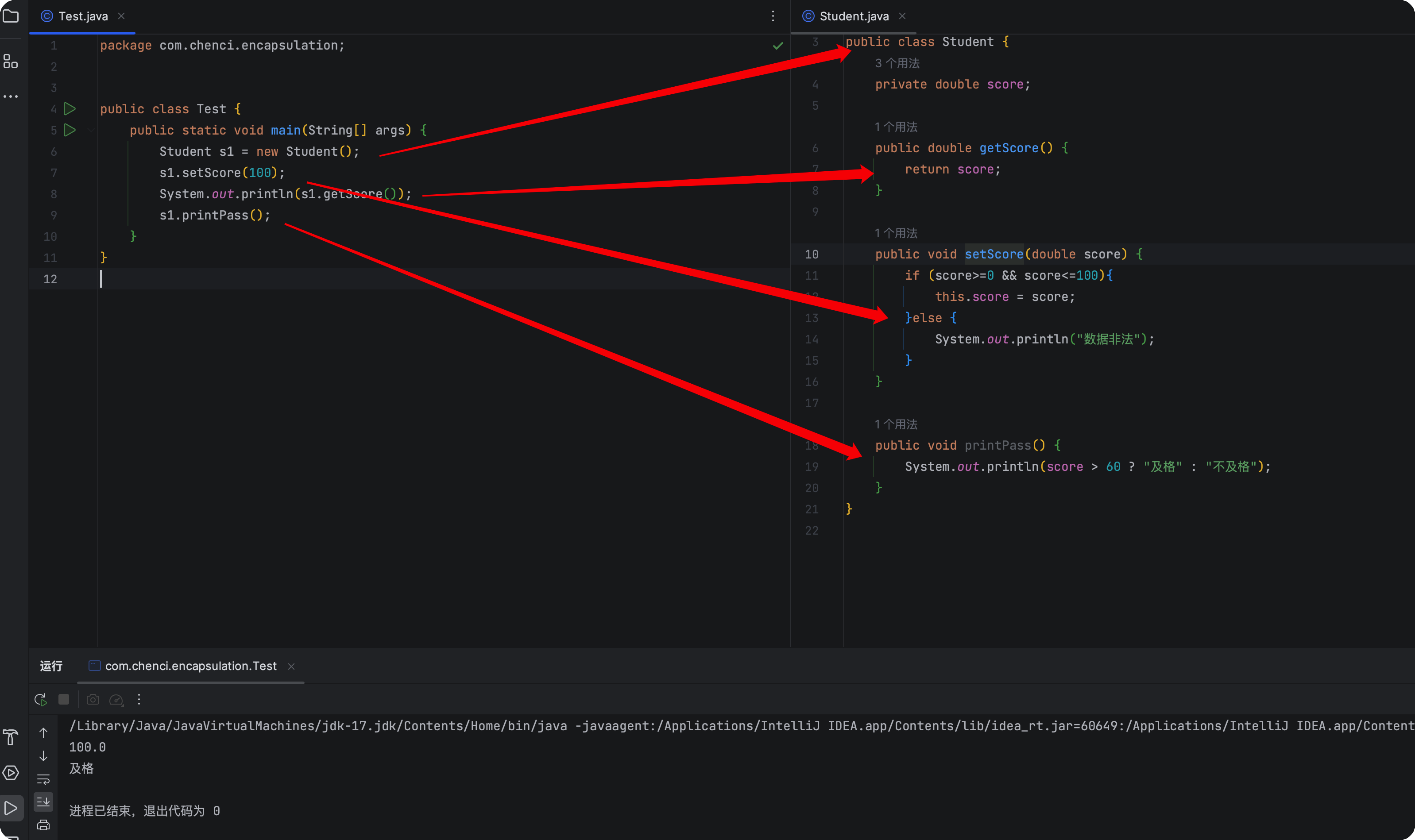

实体类
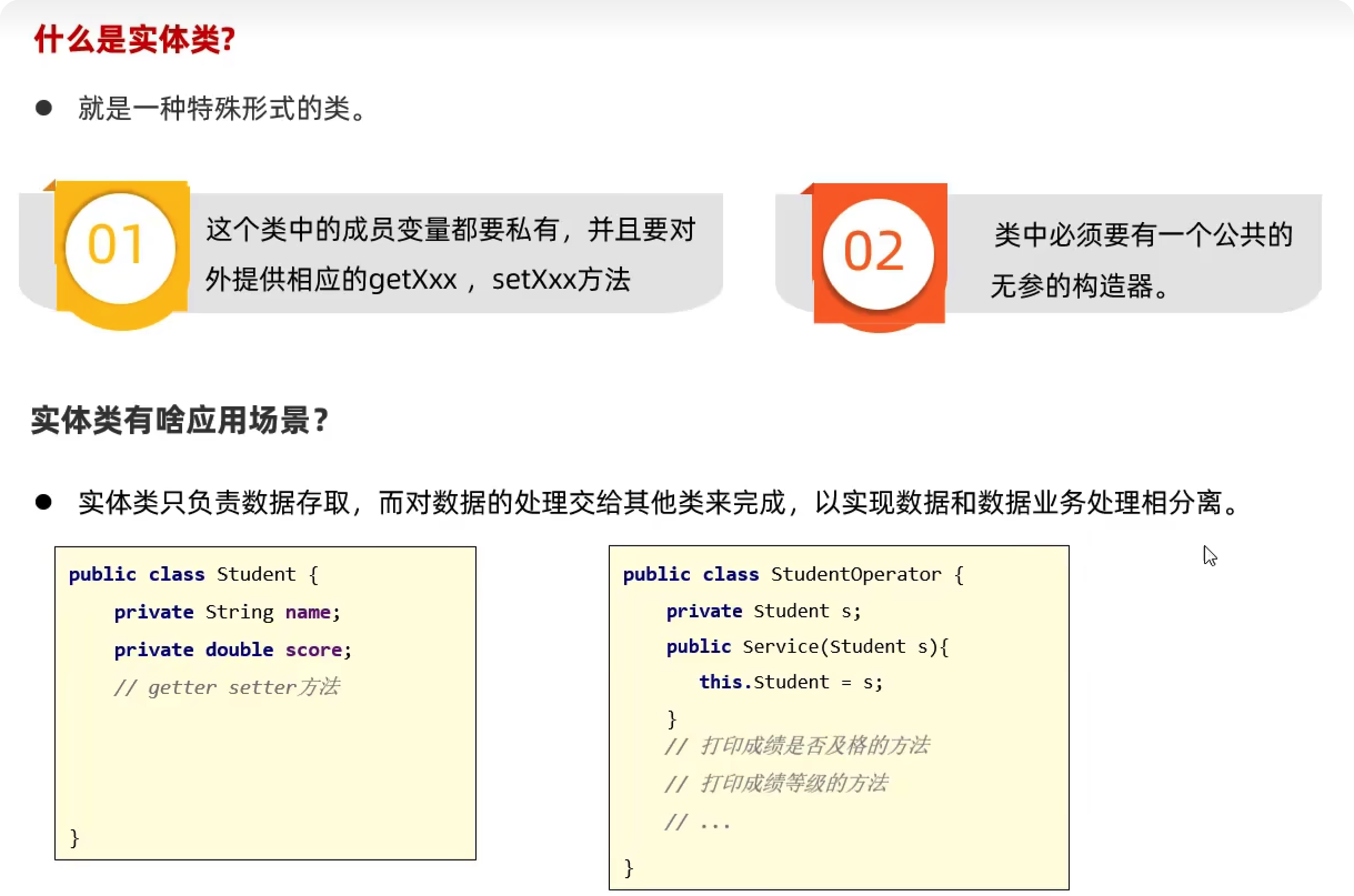

案例

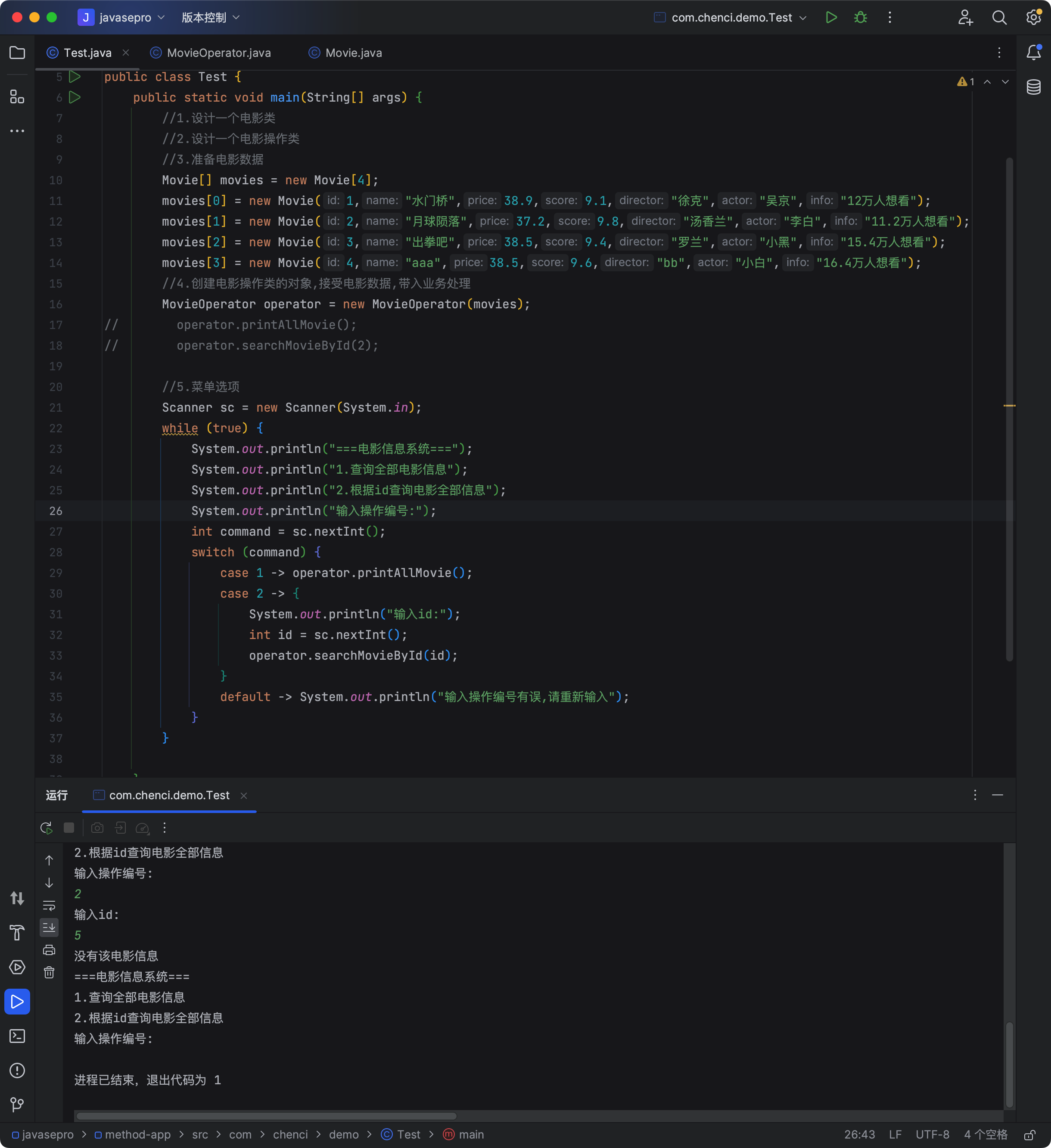
1 | package com.chenci.demo; |
1 | package com.chenci.demo; |
1 | package com.chenci.demo; |
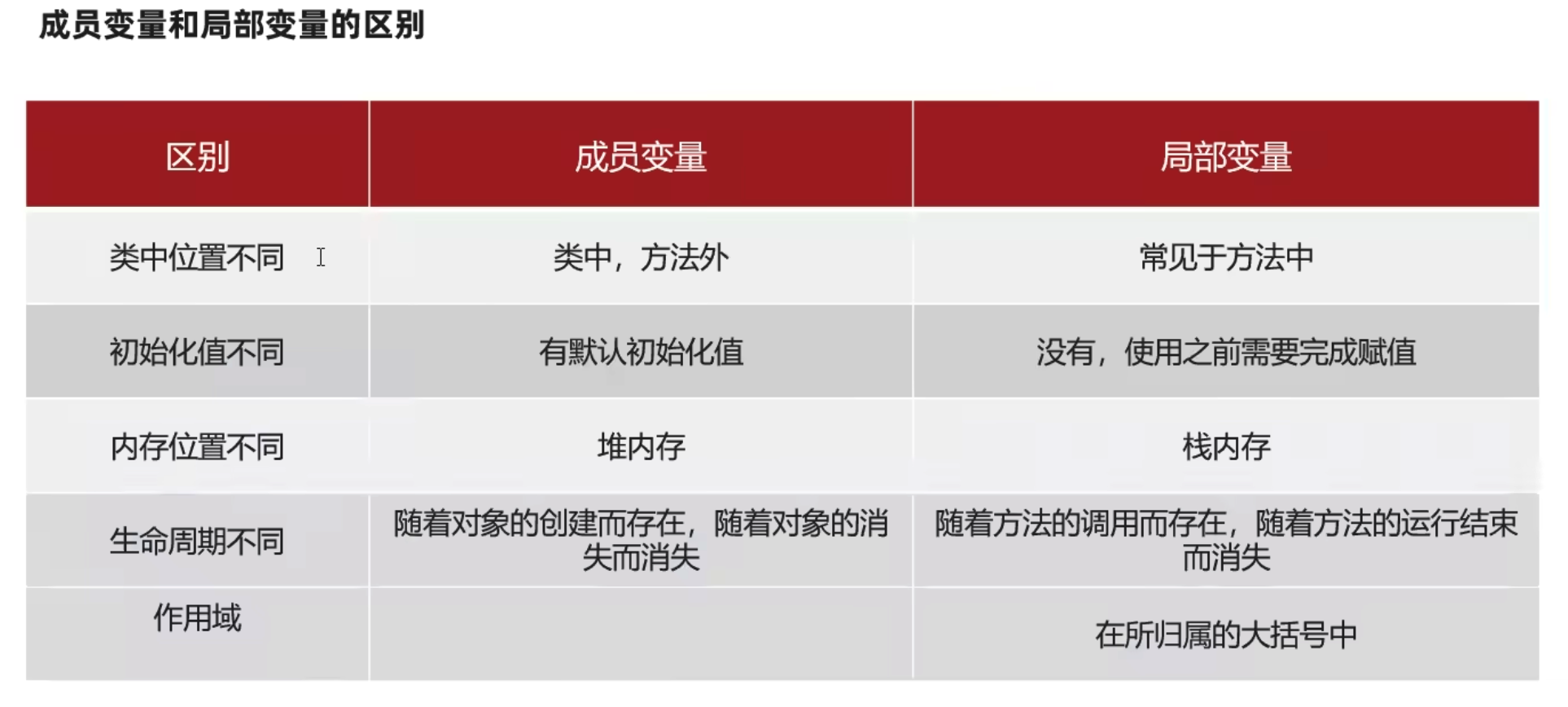
成员变量和局部变量的区别
常用api
